4.4 KiB
5G RCID
5G Remote Controlled Inspection Drone
By Sem van der Hoeven
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Installation on new flight computer
- Connecting to API
- Building PX4 firmware
- ROS2 nodes overview
Introduction
This is the code for the 5G RCID of the 5G Hub. All ROS2 nodes and the code API can be found here. The flight computer currently already contains the latest version of the software.
- The code for the ROS2 nodes can be found from the src folder (src/)
- The code API can be found from the api folder (api/)
- Further information about how the drone is built and how it works can be found in my report in the docs folder (doc/)
To add new ROS2 functionality, you can edit the code, push to the repository, pull on the flight computer and build the ROS2 workspace again. An example of how to do this is shown below:
# (On your computer) commit changes
git commit -a -m "Added new functionality"
git push
# (On the flight computer) pull changes
cd /home/ubuntu/ros2_ws
git fetch
git pull
# (On the flight computer) build workspace
colcon build --allow-overriding drone_services
# (On the flight computer) source workspace
source install/setup.bash
# (On the flight computer) restart ROS2 nodes
drone_scripts/restart_services.sh
To add new API functionality, you can do the same, but for the code in the api folder. Then, log in on the edge computer and pull the changes. The API is automatically restarted when the code is changed. If you want to manually restart the API, you can do so using the following command:
# (On the edge computer) restart API
sudo systemctl restart webserver
Connecting to API
To connect to the API, make sure you are connected to the 5G Hub network. Then, the API is located at http://10.1.1.41:8080/. When the drone is finished booting (the relais is switched on), you can connect to the drone using the Connect button.
Installation on new flight computer
The drone currently has a Raspberry Pi that contains a ROS2 installation. The Raspberry Pi runs Ubuntu 20.04 and ROS 2 Foxy. If you want to install this on a new Pi, you should get Ubuntu Server 20.04, and install ROS2 Foxy on it. Then, you should clone this repository into a 'ros2_ws' folder. You can do that using the following commands:
git clone git@github.com:etmeddi/5g_drone_ROS2.git
mv 5g_drone_ROS2 ros2_ws
After that, to make sure the connection to PX4 works, you should follow the PX4 ROS2 User Guide provided by PX4.
Building PX4 firmware
The RCID uses a custom version of the PX4 firmware to include the battery percentage and CPU load of the flight controller. Before building the firmware, make sure the developer toolchain is set up correctly. To build the firmware, first clone the repository (from the PX4 docs):
# enter home directory
cd
# clone git repository
git clone https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Autopilot.git --recursive
In the PX4 directory, edit the file src/modules/uxrce_dds_client/dds_topics.yaml. Above the line that says subscriptions:, add the following:
- topic: /fmu/out/battery_status
type: px4_msgs::msg::battery_status
- topic: /fmu/out/cpuload
type: px4_msgs::msg::cpuload
The file can also be found in this repository at dds_topics.yaml. After changing the file, you can build the firmware using the following command:
# navigate to root of PX4 directory
cd ~/PX4-Autopilot
# build firmware
make px4_fmu-v5_default
The built firmware file will be located at PX4-Autopilot/build/px4_fmu-v4_default/px4_fmu-v4_default.px4. You can then flash this to the flight controller using QGroundControl. Make sure to select the custom firmware option when flashing, and select the built firmware file.
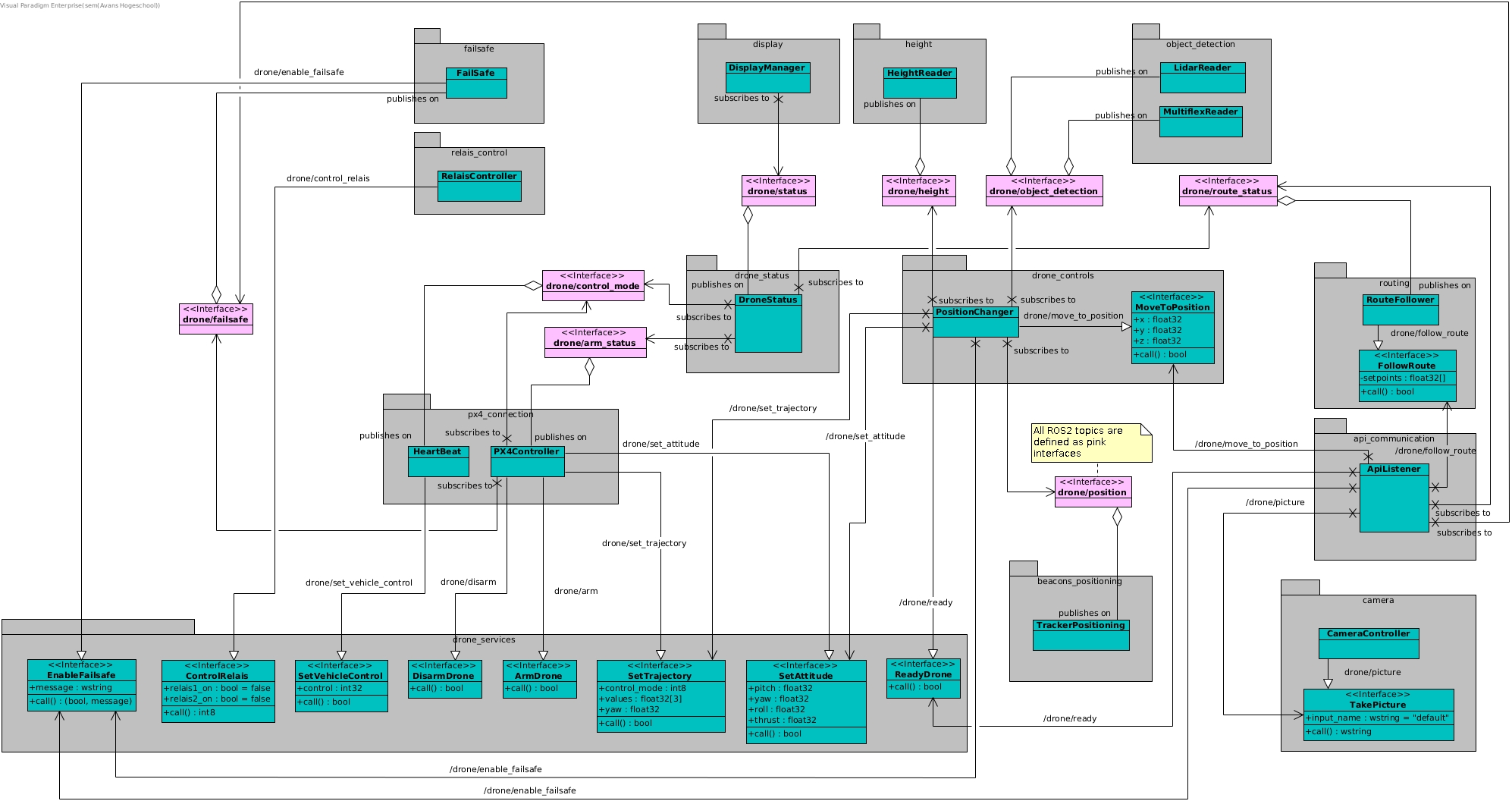
ROS2 nodes overview
An overview of all the ROS2 nodes, services and topics can be found below (also visible in my report)